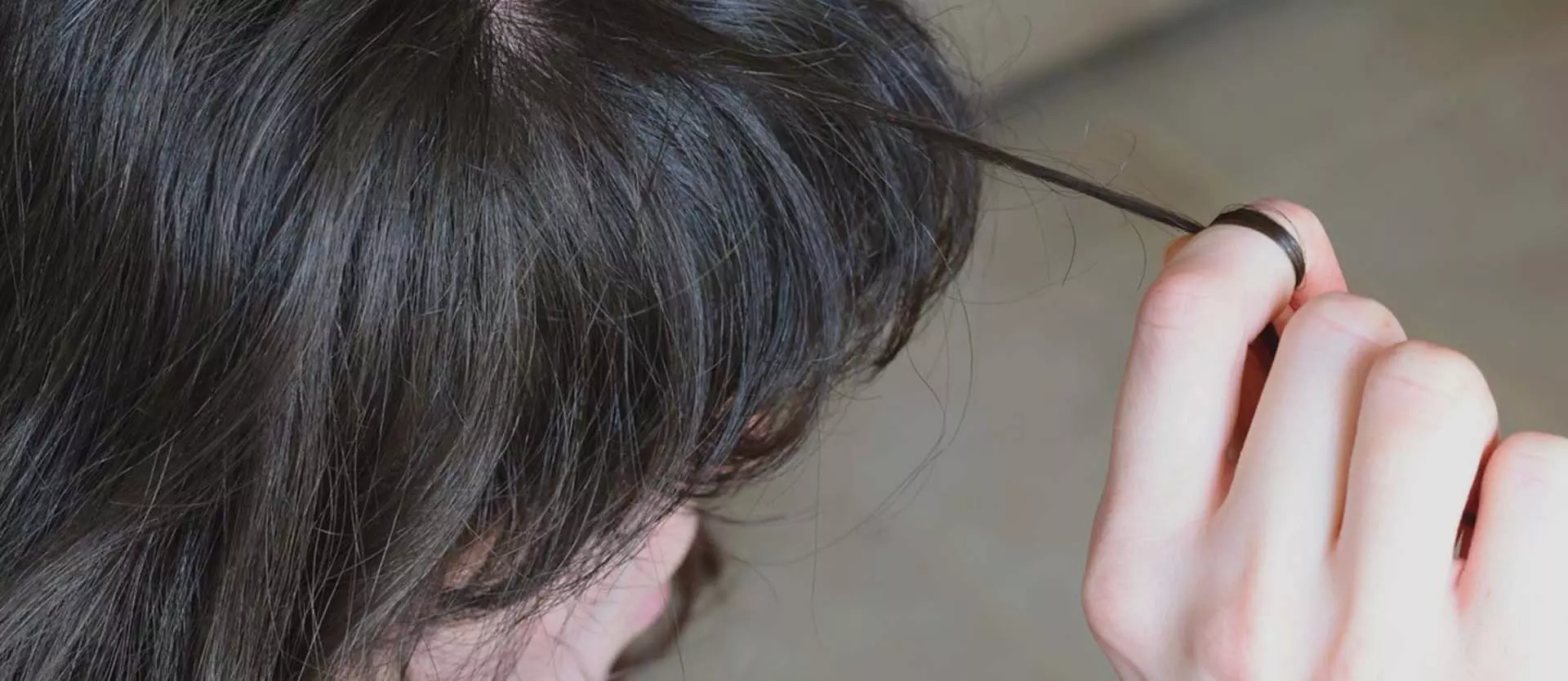
Many people experience hair loss for reasons related to health or stress. Some have a condition called trichotillomania or hair pulling. This disorder is one in which a person feels the need to pull hair out of the scalp and may sometimes do the same for other areas of the body. As a body focused repetitive behavior disorder, a person with trichotillomania wants to stop engaging in the condition but typically finds it nearly impossible to do so. They engage in recurrent as well as irresistible urges to pull their hair out.
To those who do not have this condition, it can seem strange and easily preventable. For those with it, it’s hard to manage. What’s more, the hair pulling can lead to bald patches on the scalp. Trichotillomania makes social interactions more difficult for those with this condition. Many times, people who have trichotillomania do whatever they can to hide their condition and any hair loss associated with it.
Common Signs of Trichotillomania
It may not be something people realize at first, but the symptoms of trichotillomania can be obvious to see over time as the condition worsens.
One of the most common is simply the repeated act of pulling out hair. This is generally on the scalp but may also be any other location on the body, including the eyelashes and eyebrows. A person may also feel differently throughout the process. For example, they may have tension and increasing frustration or anxiety before pulling or when they try to resist doing so. Then, after they do it, they feel a sense of relief. Many people develop a high level of hair loss in the areas where they pull. That may include thinned out hair, hair that is shortened, or bald areas where the hair does not grow back readily.
There are other signs of the condition as well, including biting, chewing, or even playing with the hair, such as rubbing it between the fingers or rubbing it against skin. This all serves as a type of pleasure for the individual engaging in this behavior.
Perhaps one of the most noted signs of trichotillomania happens when a person tries to stop engaging in this activity. They may feel a sense of distress and building up of anxiety. Many times, they may feel they need to do so, or they cannot move on with their day. When they are in high stress situations at home or work, where they cannot pull hair without being obvious, these symptoms may heighten and make them feel anxious.
How Can Trichotillomania Be Treated?
People living with trichotillomania may benefit from therapy. Cognitive therapy enables a person to recognize when they are engaging in these behaviors and to change them, minimizing the number of negative outcomes that occur. Some people may also benefit from acceptance and commitment therapy. Often, it is important to get to the bottom of the cause. This may include high stress levels or other mental health disorders that are impacting a person’s quality of life.
Often, with therapy, hair will grow back. Over time, this type of habit can right itself with a better level of support for stress and distress itself. Yet, it is nothing to ignore. Doing so may allow trichotillomania to worsen over time, and that makes it much harder to treat for those individuals. Speak to your doctor about options for therapy.
At Unique Hair Concepts, we provide a safe, comfortable and private environment for our guests living with trichotillomania. Contact the team at Unique Hair Concepts for a free, private consultation to learn more about the services offered at the center.