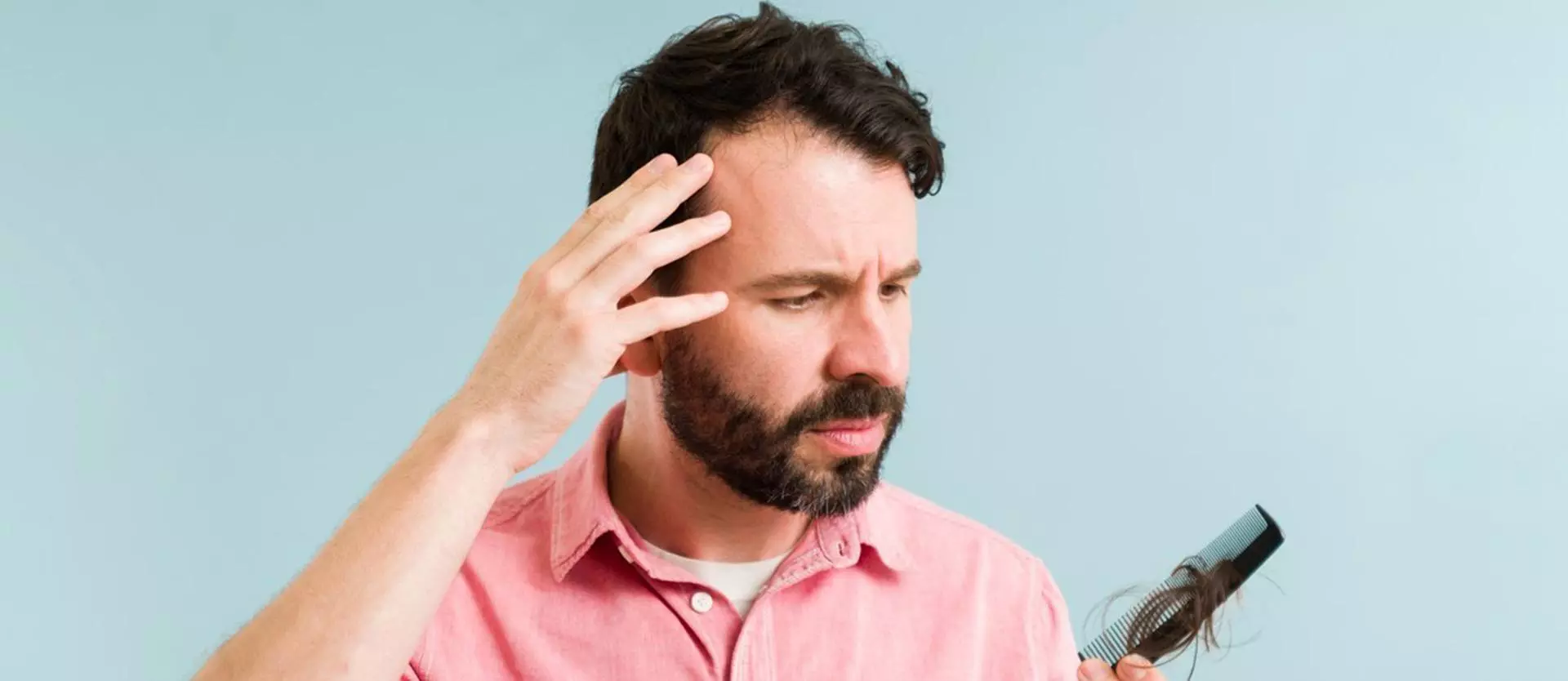
Male pattern balding, sometimes called androgenic alopecia, is a common reason men lose hair. Women can also experience hair loss like this, though it occurs less frequently – about 50 million men suffer from male pattern balding while about 30 million women suffer from female pattern balding. These tend to occur because of changes in the hormones in the body. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is one of those concerns. How can it impact hair loss for you?
What Is DHT?
DHT is an androgen, a type of sex hormone that contributes to the male sex characteristics such as body hair development. However, DHT may lead to early hair loss in some people.
DHT comes from testosterone, a hormone that both men and women have. DHT contributes to increased body hair and muscle production, as well as how fat is stored in the body.
As a person gets older, the amount of DHT and testosterone they have changes. That is often evident in changes to muscle mass in men as they age as well as overall sexual health.
DHT moves through the body’s bloodstream linking to receptors on hair follicles on the scalp. When this happens, it may cause the follicles to shrink and become too small to grow hair. This typically happens in people as they age.
DHT can cause hair loss, then, but it can also cause other risk factors for many people, such as an increased risk of prostate cancer, coronary heart disease, and slow healing of the skin.
Is It Genetic?
There are a lot of factors that are unknown about DHT and how it works in the body. However, there is a strong link between genetics when it comes to the onset of hair loss. If you have close family members – such as your mother or father – who have had pattern baldness and it was due to DHT levels, that could mean you are at a higher risk of this occurring as well. Many times, this is the main reason for male pattern baldness in men – it is a genetic factor passed down from one generation to the next.
The Science of DHT and Balding
The hair follicles on your skin are small areas of tube-like structures in which a single strand of hair grows. They are located throughout your body. The follicle allows a hair to go through the growth cycle, which typically lasts between two and six years. During that time, the hair goes through phases of growth and rest.
At the end of the cycle, the hair enters a resting phase. Then, a few months later, it will fall out naturally. This is not worrisome and is necessary. Over a few months after this, a new hair begins to grow in place of the old.
All of this can be impacted by androgen levels. If your DHT level is too high, it can cause the hair follicles to shrink in size. As that happens, it can force the thinning of the hair until it breaks and falls out. Also, DHT levels can impact the length of the hair growth cycle, meaning that your hair will fall out sooner than expected. It also makes it much more difficult for new hair to grow in, which can make it seem like you have hair loss.
Why does this happen to some people more than others? One factor is that genetics impacts the way that androgen receptors react. For example, some people are simply more sensitive to DHT. The androgen receptor gene variations can lead to the hair being able to grow and thrive or being more likely to fall out.
Reducing DHT
The only way to reduce the effect of this is to reduce DHT production. There are numerous medications that may help with this process. These typically will target the DHT production and receptor binding. This includes blockers and inhibitors. Some of these products are called Minoxidil and Finasteride.
There are some alternative treatments that may offer help as well, including increased biotin use, pumpkin seed oil, and pygeum bark. The use of serenoa repens, an all natural alternative has shown to be beneficial and without side effects.
If you suspect your hair loss is due to genetic factors, it may seem like there is nothing you can do. That is not always the case. Reach out to your doctor to talk about the use of preventative treatments to slow down your hair loss or thinning hair. You may also want to meet with a hair specialist to learn about the various options for hair loss prevention.